Why Learn Time series forecast
My current company BoostMyShop, an e-commerce company offers a variety of SaaS applications to help e-commerce sellers grow their businesses. One of our products, MyPricing, is a market monitoring and repricing application that helps sellers stay competitive in the market.'
Recently, I've been intrigued by the potential of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) in improving our applications. I realized that time series prediction could be a valuable addition to MyPricing, so I decided to learn how to implement it.
Data Preparation
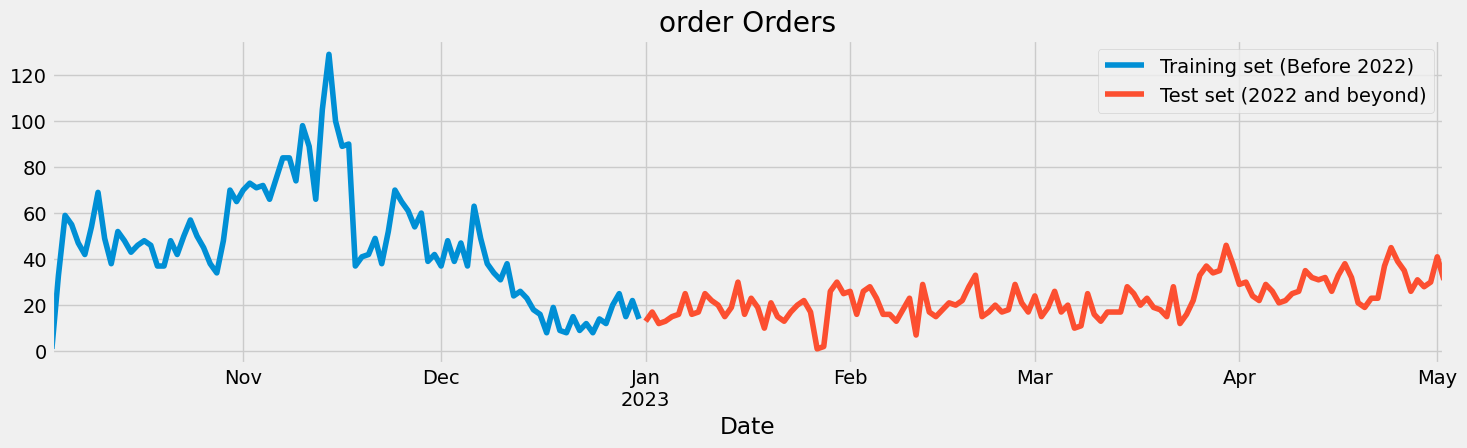
I started by exporting order history data from MyPricing into a CSV file, which I then used as the dataset for my experiments.
I split the dataset into training and testing sets, allowing me to train the models on one portion of the data and evaluate their performance on another.
Different Time series models
During my research, I came across several ML models that are commonly used for time series prediction. These models use historical data to make predictions about future values of a variable, in this case, number of orders . Each of the models has its own strengths and weaknesses, so I decided to implement and compare them to determine which one would be the best fit for MyPricing.
1. Single Layer Small RNN (Recurrent Neural Network)
The Single Layer Small RNN is a simple model with a single recurrent layer. This layer allows the model to take into account previous values in the time series when making predictions. The model is relatively easy to understand and implement, making it a good starting point for exploring time series prediction with ML.
2. Single Layer RNN
The Single Layer RNN is similar to the Small RNN but with more neurons in the recurrent layer. This model is expected to have better performance due to its increased complexity. The model can capture more complex patterns in the data and make more accurate predictions.
3. GRU (Gated Recurrent Unit) with dropout
The GRU with dropout model is a more advanced model that includes a gating mechanism to control the flow of information through the network. The dropout layers help prevent overfitting, making the model more robust. The model is able to capture dependencies in the data and make predictions that are more accurate thanthe simpler models.
4. Multi-layer RNN
The Multi-layer RNN model consists of multiple recurrent layers stacked on top of each other. This model can capture even more complex patterns in the data than the Single Layer RNN, potentially leading to better predictions. The model is able to learn hierarchical representations of the data, which can be useful for modeling complex time series.
5. GRU
The GRU model is similar to the GRU with dropout but without the dropout layers. This model is known for its ability to capture long-term dependencies in the data, making it a strong candidate for time series prediction. The model can learn and remember long-term patterns in the data, which can be useful for predicting trends over longer time periods.
All of these models can be trained on the historical order data to make predictions about future number of orders.
Models Evaluation
Once I had implemented all the models, I trained them on the training dataset and evaluated their performance on the testing dataset.
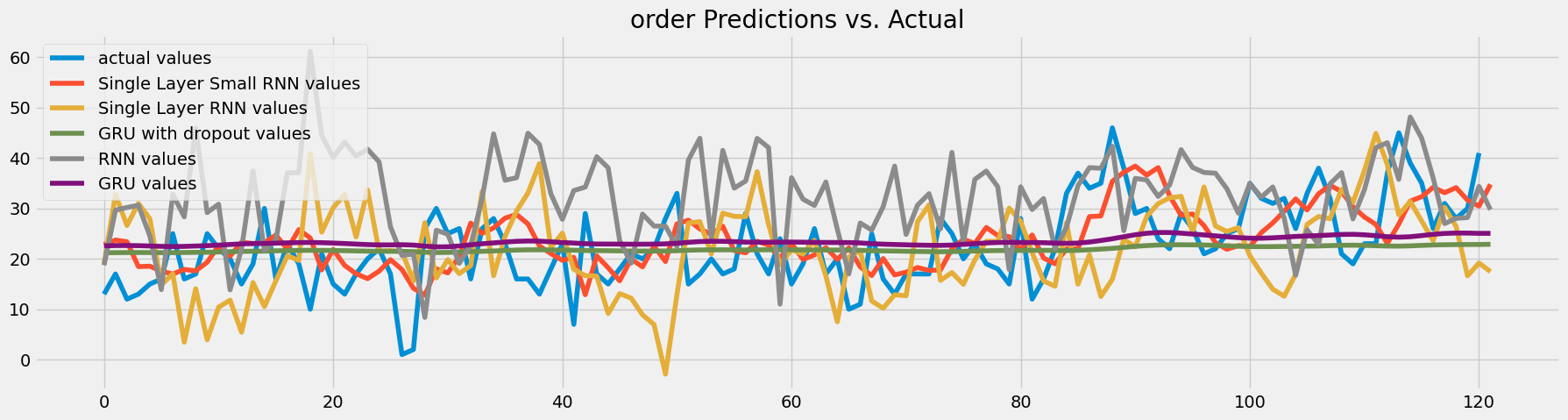
To visualize the results, I plotted the actual number of orders and the predictions from each model.
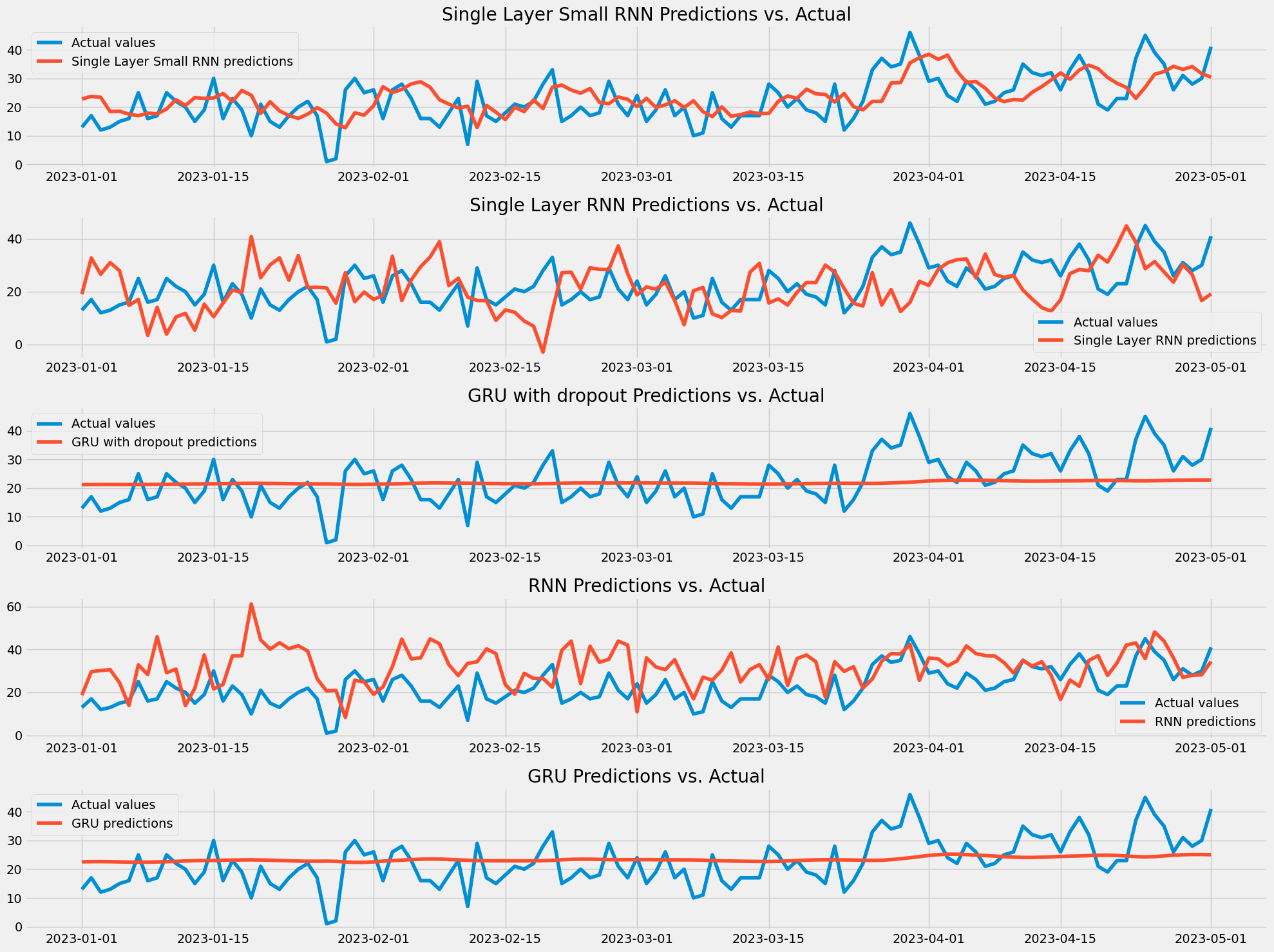
We have the visualization, but how can we determine the performance of each model? Welcome to the Mean Squared Error (MSE)
Mean Squared Error (MSE)
Mean Squared Error (MSE) is a way to measure how well a regression model (like a time-series forecasting model) is able to predict a set of values. It calculates the average of the squared differences between the predicted values and the actual values.
A smaller MSE value means that the model is better at predicting the actual values.
Think of it like a score, where a perfect score is 0, and the higher the score, the worse the model performs.
| Model | MSE |
|---|---|
| Single Layer Small RNN | 56.992458 |
| GRU | 62.361303 |
| GRU with dropout | 63.860396 |
| Single Layer RNN | 141.982957 |
| RNN | 217.592279 |
Lesser the MSE => Smaller is the error => Better the accuracy
Based on the Mean Squared Error (MSE) metric we got, Single Layer Small RNN had the lowest error and performed the best for the number of orders prediction task in general. However, it's important to note that the performance of the models can vary depending on the specific dataset and problem being addressed.
In my particular experiment, the Single Layer Small RNN performed the best. It's possible that the data had a simpler pattern that the Single Layer Small RNN was able to capture effectively, while the more complex models may have overfit the data or not been able to capture the relevant patterns as well. Additionally, the Single Layer Small RNN is a simpler model than the other models, which can be an advantage in terms of computational resources and ease of implementation.
While more complex models may have the potential to perform better on more complex datasets, simpler models like the Single Layer Small RNN can still provide effective solutions in certain cases.
when working with machine learning models, it's important to evaluate their performance on multiple datasets to ensure that the model is robust and effectivein a variety of scenarios.
Learning outcomes
During this project in time series prediction, I learned how these technologies can improve e-commerce applications. I discovered that choosing the right ML model is crucial for solving specific problems and datasets. By testing multiple models, I gained hands-on experience with their strengths and weaknesses and learned how to balance complexity and performance.
I also learned the importance of evaluating model performance on multiple datasets to ensure that the model is effective in different scenarios. Overall, this project expanded my knowledge and skills in AI and ML.
